 |
 |

|
|
|
| PO |
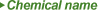 |
| Propylene oxide |
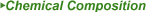 |
| Propylene Oxide |
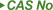 |
| 75-56-9 |
 |
Propylene oxide (PO) is a commodity chemical used as a building block in the production of derivative products, including polyols, propylene glycols (PG), propylene glycol ethers (PGE) and various other chemical products.
Based on published data, worldwide demand for PO was approximately 7.8 billion pounds (3500 KT) in 1995.
Approximately 90 percent of that volume was consumed in the manufacture of three derivative families of products: polyols, PG, and PGE. Other PO derivative chemicals are butanediol, propylene carbonate, allyl alcohol, modified starches, and surfactants. |
 |
Specific Gravity: 0.829-0.831 @ 20/20'C
Distillation @ 760 mmHg: IBP, 'C ('F)-33.0 (91), min., DP, 'C ('F)-37.0 (99), max.
Acidity: 0.002 wt % as acetic acid, max.
Aldehydes: 0.010 wt % as propionaidehyde, max.
Water: 0.020 wt %, max.
Total Chlorides: 0.001 wt % as Cl, max.
Color: 5 platinum-cobalt, max.
Non-volatile Matter: 0.002 gms/100 ml, max.
Suspended Matter: Substantially Free
Formula Weight: 58.08
Density @ 25'C (77'F): 6.86 lb/gal
Flammability Limits in Air@ 25'C (77'F): 1.7-36 vol %
Flash Point, Tag Closed Cup, 'C ('F): < -37 (< -35)
Solubility@25'C(77'F) : Propylene Oxide in Water - 40wt%, Water in Propylene Oxide - 13wt%
Refractive Index np25: 1.3632 |
|
|
|
|
|










