 |
 |

|
|
|
| Boron B ¡Ã93 |
 |
| BORON (BORON AND BORATES ONLY) |
 |
| Total Boron(B) content,£¥:¡Ã93 |
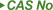 |
| 7440-42-8 |
 |
| Uses£ºBoron is mainly used in metallurgy, electronics, medicine, ceramics, nulear industry and chemical industry etc, it is used in the form of compound or is added in some alloys as a addend. It can be used in smelting of some special alloy steels and as the gas remover for the melting steel, in the burn-entraining pole of burning-entraining tube in the electric industry, in the control stick of atomic reactor, and in the high-energy fuels for rocket. It is a important material for making high-pure halogenated borons, also a material for making a variety of boronic compounds. A lot of noble and rare metals can be substituted and saved by it. Boron and its compounds can be also used as the catalyst for some organic chemical reactions, and so on. |
 |
Total Boron(B) content,£¥ ¡Ã93
Water soluble Boron(B) content £¥:¡Â0.8
PH value 4.0-5.5
Moisture content, £¥:¡Â1.0
Appearance(see with eyes) Pale brown or brown-black amorphous powder
Physical and chemical properties£º
1.1 Elementary symbol£ºB
1.2 Atomic weight£º10.81(on 1979 international atomic weight)
1.3 Melting point£º2300¡¾2¡É
1.4 Sublimation temperature£º2550¡É
1.5 Specific gravity£º2.34-2.37
1.6 Solubility£º It is undissolved in water, hydrochloric acid, ethanol and ethyl ether, but dissolvable in cold concentrated basic solution and decomposed, hydrogen is release at the same time. It can be oxidized by concentrated sulfuric acid or nitric acid to boric acid.
1.7 Properties£º Boron is on a special place in the mid of metal and nonmetal on the periodic table of elements. Its chemical properties are more active because of very strong negative electricity, small atomic radius and centralized nuclear charge. It is stable in normal temperature, oxidized when heating to 300¡É,and burned if heated to 700¡É.It is tasteless and odorless. Its nonmetal property is similar to silicon. Boron can interact with oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, halogen or carbon etc. It can be combined directly with many sorts of metals to form the boronic compounds. Moreover boron can be also reacted with organic compounds to generate some compounds, in which boron is directly joined to carbon, or oxygen exists between boron and carbon. |
| Industrial field |
additive |
|
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
| There are no existing companies to distribute selected chemical product |
|
 |
|
|
|










